中文名称:小鼠抗COX4I1单克隆抗体

|
Background: |
Cytochrome c oxidase (COX) is the terminal enzyme of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. It is a multi-subunit enzyme complex that couples the transfer of electrons from cytochrome c to molecular oxygen and contributes to a proton electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. The complex consists of 13 mitochondrial- and nuclear-encoded subunits. The mitochondrially-encoded subunits perform the electron transfer and proton pumping activities. The functions of the nuclear-encoded subunits are unknown but they may play a role in the regulation and assembly of the complex. This gene encodes the nuclear-encoded subunit IV isoform 1 of the human mitochondrial respiratory chain enzyme. It is located at the 3' of the NOC4 (neighbor of COX4) gene in a head-to-head orientation, and shares a promoter with it. Pseudogenes related to this gene are located on chromosomes 13 and 14. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. |
|
Applications: |
WB, FC, IF, IP, IHC |
|
Name of antibody: |
COX4I1 |
|
Immunogen: |
Fusion protein of human COX4I1 |
|
Full name: |
cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4I1 |
|
Synonyms: |
COX4; COXIV; COX4-1; COXIV-1; COX IV-1 |
|
SwissProt: |
P13073 |
|
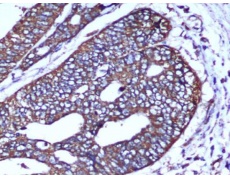
IHC positive control: |
Human colorectal carcinoma |
|
IHC Recommend dilution: |
25-50 |
|
WB Predicted band size: |
20 kDa |
|
WB Positive control: |
Mouse skeletal muscel tissue and Jurkat cell lysates |
|
WB Recommended dilution: |
1000-5000 |
|
IF positive control: |
Hela cells |
|
IF Recommend dilution: |
50-150 |
|
FC Recommend dilution: |
50-100 |



 购物车
购物车 帮助
帮助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009